TM 5-2420-230-10
1-14. ENGINE SYSTEM.
a. Air Intake. The air intake system consists of a dry-type air cleaner (1), a turbocharger (2), and an aftercooler (3).
Engine exhaust gases flow through the turbocharger (2) driving a turbine wheel. A compressor wheel on the opposite
end of the turbine wheel shaft rotates and draws in fresh air through the air cleaner (1). Air from the air cleaner (1) flows
through the aftercooler (3) which cools the air before it is delivered to the engine cylinders.
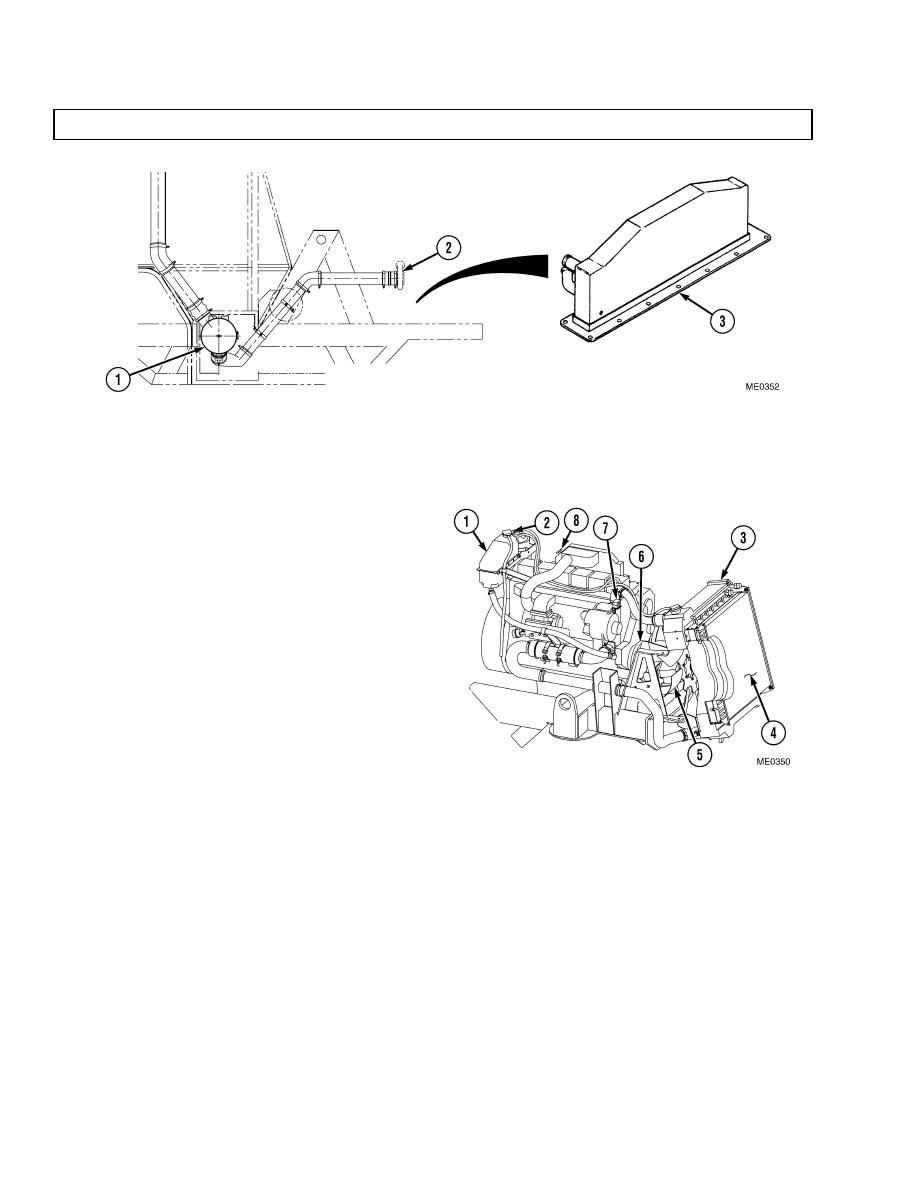
b. Cooling System. The pressure-type cooling
system protects the engine by removing heat
generated during the combustion process. Coolant
is added to the coolant reservoir (1) through the
filler cap (2). Pressure within the cooling system
is regulated by pressure releases in the filler
cap (2) and a relief cap on the radiator. Hot
coolant flows from the engine to the top radiator
tank (3) and through the radiator core (4), where a
stream of air removes heat. This air is drawn
through the cores by a hydraulically activated
fan (5). A water pump (6) draws the coolant from
the bottom of the radiator and pushes it through
the engine, repeating the cooling process.
Thermostats (7), mounted in each coolant outlet
elbow, remain closed until the coolant approaches
a predetermined temperature, at which time they
open. When the coolant temperature drops below
the thermostat rating, they close. An air vent
line (8), between the radiator (3) and the water
pump inlet, removes air trapped in the engine
when the cooling system is being filled.
c. Fuel System. Fuel is drawn from the fuel tank by the fuel pump. It passes through the supply line to a fuel/water
separator (Primary Fuel Filter) and a secondary fuel filter to the engine fuel injector pump. There, fuel is metered and
sent to the six fuel injectors via the fuel injector lines. Surplus fuel from injectors is returned to the fuel tank through the
return line. The fuel/water separator removes water and large solid particles from the fuel. The finer particles are
removed by the secondary filter before they can enter the fuel injector pump.


