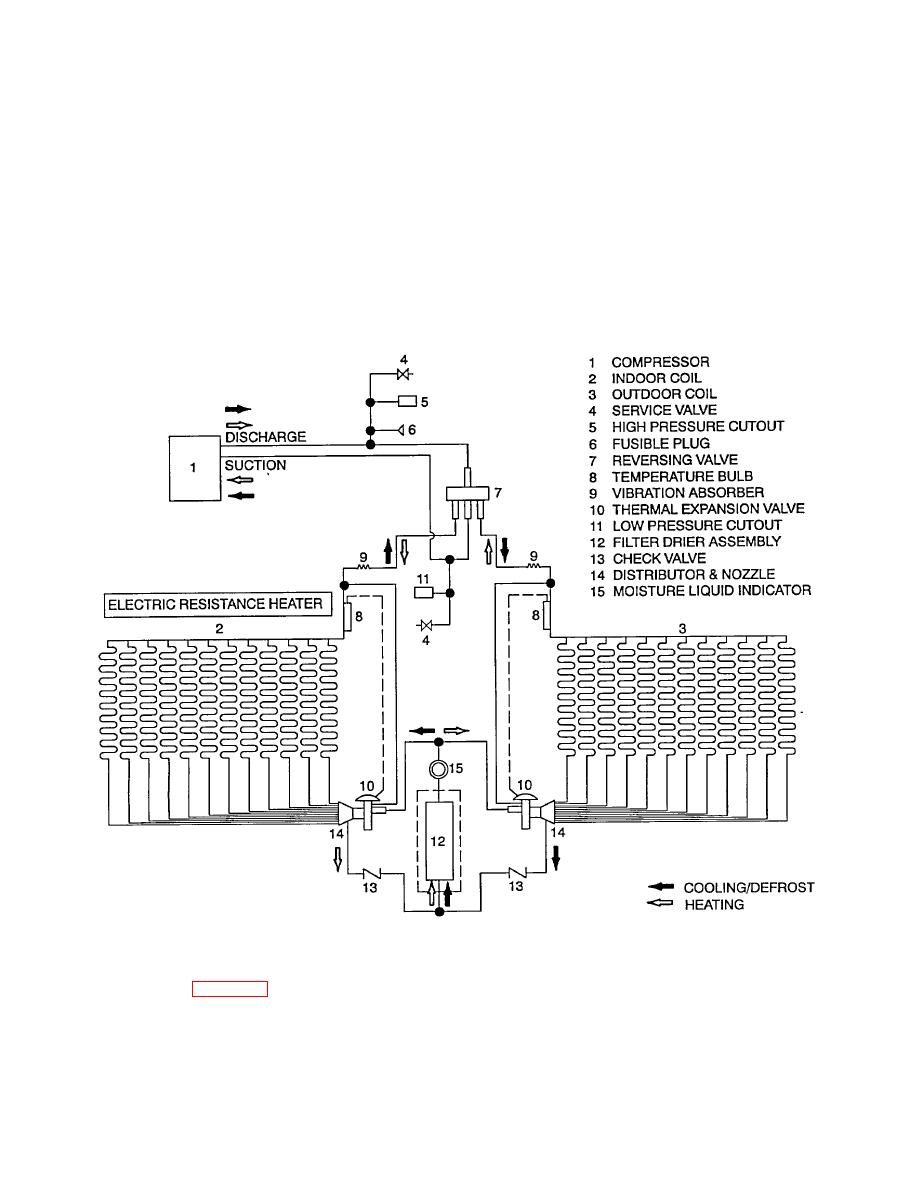
TM 9-4120-411-14
1.17.7 The high pressure liquid then passes through the liquid indicator (15) where the condition of the refrigerant can be
visually inspected.
1.17.8 The outside expansion valve (10) inlet and outlet pressures are equal in this mode of operation preventing flow
through it. The high pressure liquid will then pass through the inside expansion valve (10) which causes a pressure drop
and automatically meters the amount of liquid passing through it. The rapid drop in pressure causes the liquid to cool.
1.17.9 The cool, low pressure liquid passes through the inside coil (evaporator) (2) where heat is absorbed from the
shelter air passing across it causing the low pressure liquid to evaporate to a low pressure gas. The low pressure gas
then returns to the compressor (1) to begin the cycle again.
1.17.10 When the shelter air passes across the inside coil (2) it will be dehumidified. This is a result of the rapid drop in
temperature causing moisture to condense out of the air and collect on the coil.
Figure 1-6. Cooling, Dehumidifying, and Heating System Schematic
1.18 HEATING. See figure 1-6.
1.18.1 Air is heated primarily by a reversing mechanical refrigeration system called a heat pump. Supplemental electric
resistance heat is provided for use during system defrost mode and operation in low ambient temperature conditions.
1-11


